
25th European Congress of Psychiatry / European Psychiatry 41S (2017) S847–S910
S881
strategies to resist social pressure to drink; and build positive
strategies for coping with stress.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.01.1778EV1449
A comparative research of therapy
regimens related to patients with
alcohol addiction syndrome for the
period 2000–2009 in narcological
clinical hospital No. 17 of Moscow
B. Tsygankov
∗
, S. Shamov , M. Zemskov
Moscow State Medical Dental University, Department of Psychiatry,
Narcology and Psychotherapy, Moscow, Russia
∗
Corresponding author.
The incidence rate of alcohol addiction syndrome continues to
increase worldwide. In the Russian Federation, there is a priority
of the patient’s rights for an effective and safe treatment of narco-
logical disease. This is achieved using standardised, reproducible,
statutory narcological patients diagnosis and management stan-
dards.
Research purpose
Identify efficient algorithms for alcohol addic-
tion syndrome treatment in a Narcological Clinical Hospital No. 17
of Moscow (NCH
№
17), allowedNarcological patients Diagnosis and
Management Standards for the period 2000–2009.
Research objectives
(1) Identify the key therapeutic treatment
algorithms that were used in NCH
№
17 of Moscow in the period
2000–2009. (2) Compare the effectiveness of therapeutic regimens
identified.
Data for study – hospital sheets of patients treated from 2000
to 2009 in NCH
№
17 of Moscow. Analyzed 520, included in the
research: 401 hospital sheets of 118 patients.
Methods
(1) Continuous sampling. (2) Statistical, Fisher’s exact
test, Microsoft Excel software (version 13.1.) and Statistica 5.1.
Results
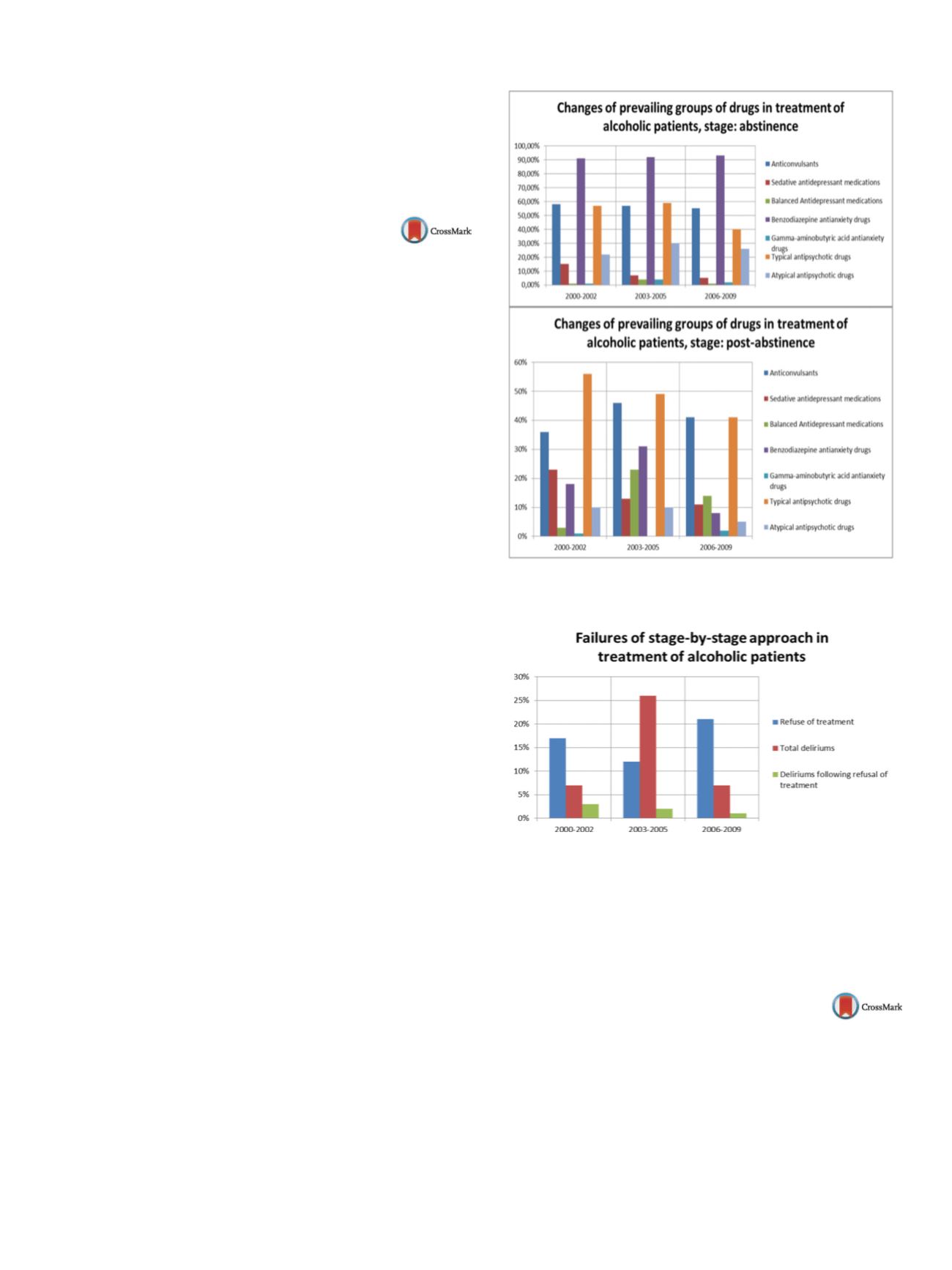
From 2000 to 2009 (1998, 2003 and 2005) have changed
three times: legislative framework, focus, narcological patients’
treatment regulation
( Fig. 1 ).Therapeutic algorithm was considered successful if the stage-
by-stage approach was complied with. Algorithm inefficiency
is designated as “failure of treatment stage-by-stage approach”.
Disadvantages of therapeutic regimens lead to complications.
Polypragmasy influenced the development of complications. From
the analyzed 118 hospital sheets (pursuant to Fisher’s exact test), 72
patients had polypragmasy, 40% cases – proven causewas delirium,
20% – refusal of treatment
( Fig. 2 ).Fig. 1
Periods of application of different regimens are outlined:
2000–2002, 2003–2005, 2006–2009.
Fig. 2
Surrogate variable of complications is refused treatment.
Disclosure of interest
The authors have not supplied their decla-
ration of competing interest.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2017.01.1779EV1450
Methamphetamine-induced
choreoathetosis: A case report
M.L. Turk
∗
, J. Smith
University of Virginia Health System, Psychiatry, Charlottesville, USA
∗
Corresponding author.
We describe the case of a 23-year-old male with a past psychiatric
history of Obsessive Compulsive disorder, Generalized Anxiety Dis-
order, Cannabis Use Disorder, and a reported history of Bipolar II
Disorder and ADHD, and no past medical history, who presented
to the hospital for a psychiatric evaluation of erractic behavior.
Per his family’s report, the patient has not been attending to his
activities of daily living and has had poor sleep and significant


















